How to Tell Which Star Is Closest Using Stellar Parallax
Stellar Parallax is the apparent shift of a close star in relation to distant stars thats caused by a change in the position of the observer. This method is very precise for measuring stellar distances but only works for nearby stars.
The average EarthSun distance or Astronomical Unit AU is 149 597 870 700 m.

. What would make stellar parallax easier to observe. It is 1 parsec closer than Star B. What would the parallax angle in arcseconds be for this binary star.
Thats about how far the closest star to the Earth is. Stellar parallax exists only because Earth orbits the Sun. Which star is closest to Earth and by how much.
D pc 1 p arcsec. The parallax angle is 0001293. Before they knew any stellar distances how did they know which stars were in the foreground Paul H BangorYour excellent question is.
The stars are not actually moving they just seem like they are because the person looking at them has moved to a different location. Stellar parallax values published by Struve Henderson and Bessel between 1838 and 1839. Star A has a parallax angle of 082 arcseconds and Star B has a parallax angle of 045 arcseconds.
1264 034 arcseconds. The parallax angle is 0002790. In fact this method only lets us measure distances to less than 1 of the stars in our own galaxy.
Some well-known examples of distance measurement by parallax are 61 Cygniat 13 of an arcsec distance 3 parsecs and Barnards Starat 18 parsecs 59 light years. The baseline used for the triangulation is fixed by the size of Earths orbit around the Sun. What would the parallax angle in arcseconds be for this binary star.
Astronomers can determine the distances to the closest stars by measuring their parallax angles. Astronomers estimate the distance of nearby objects in space by using a method called stellar parallax or trigonometric parallax. And Alpha Centauri is the closest star system to.
This stellar distance and parallax calculator determines the distance to a nearby star in light-years and parsecs from its stellar parallax measured in arcseconds and vice versa. For nearby stars we use trigonometric parallax to determine their distance. You could imagine as you go to further and further stars.
Which star is closest to Earth and by how much. To find the point of Barnards Stars closest approach to the Sun extend the diagonal of the space velocity to show the path the star will take. It is 1 parsec closer than Star B.
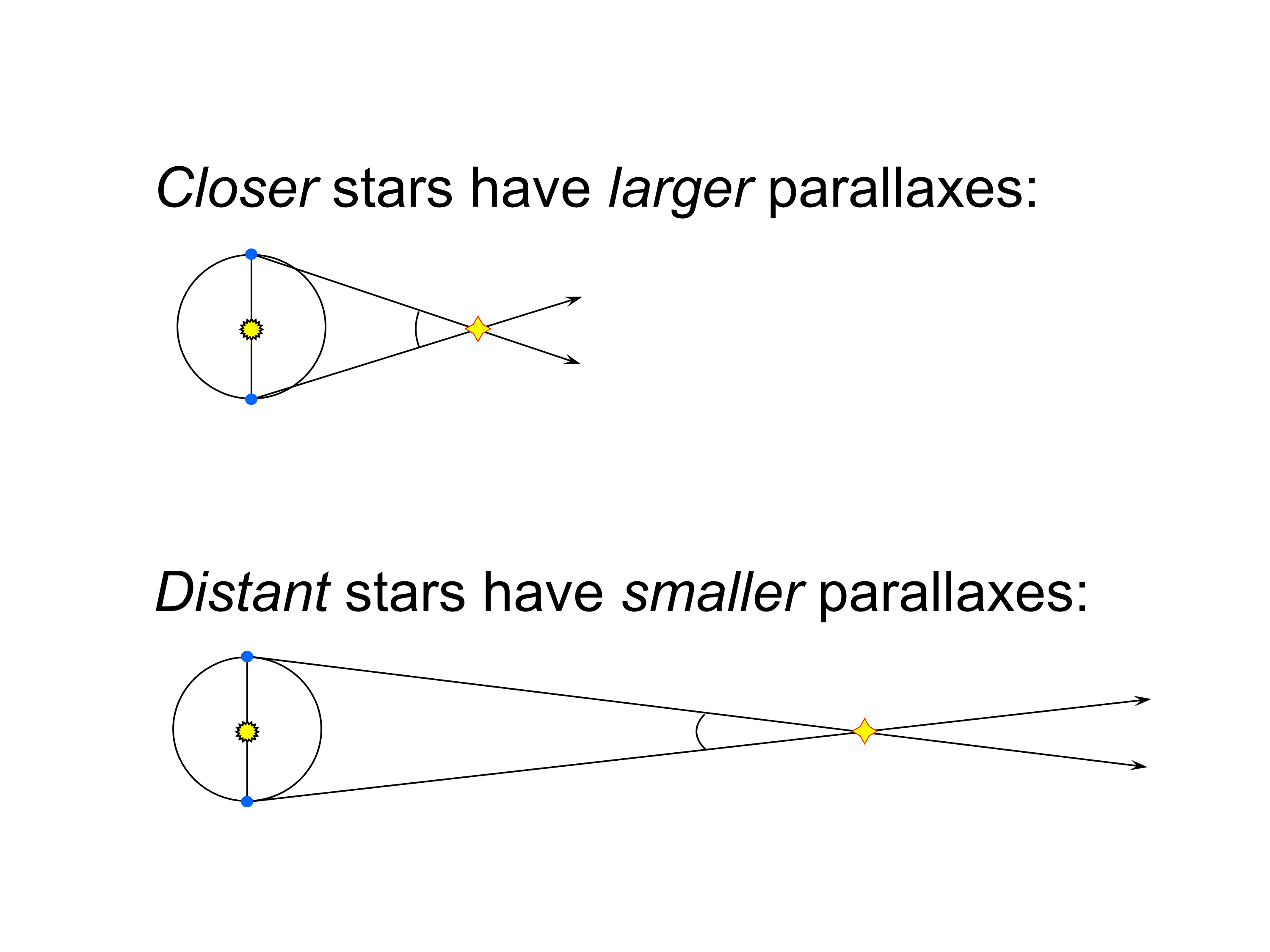
So parallax is inversely proportional to the distance the greater the distance the smaller is the parallax. Star A has a parallax angle of 082 arcseconds and Star B has a parallax angle of 045 arcseconds. The closer a star is to us the more parallax it exhibits.
10723 138 parsecs 1264 034 arcseconds Star A is closest to Earth. Simply put they measure a stars apparent movement against the background of more distant stars as Earth revolves around the sun. Define one parsec pc as the distance.
How would you use the parallax formula to determine the distances to a star in parsecs. Stellar distance using parallax. As a result we need another method to measure distances to stars.
Even for the nearest stars parallax angles are too small to measure with the naked eye. As far as I know direct parallax measurements are the only way to directly measure the distances to stars. In astronomy it is an irreplaceable tool for calculating distances of.
Measurements of these stellar movements can be used to determine the distances to the stars. Using a ruler and a protractor find the point along this line where Barnards Star is closest to the Sun. Displaystyle d text pcapprox 1p text arcsec For example Proxima Centauri the nearest star to Earth other than the Sun whose parallax is 07685 is 1 07685 parsecs 1301 parsecs 424 ly distant.
One of the most popular is the method known as Stellar Parallax the use of trigonometry to determine distance. Parallax in observing stars. How does stellar parallax work.
August 28 2021. Calculate the distance in light years to the brightest star in the Northern celestial hemisphere Arcturus α Boötis in the constellation of Boötes from its parallax value of 8883 milliarcseconds. And so the closest star of the Earth has this very very very apparent a very small change in angle.
The approximate distance is simply the reciprocal of the parallax. 10723 138 parsecs. A line connecting the sun and point of closes approach should be perpendicular to the.
Parallax is the observed displacement of an object caused by the change of the observers point of view. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. Knowing baseline 2 AU allows us to calculate the distance.
Known as parallax this movement is larger for nearby stars and smaller for more distant stars. Look at apparent motion of object against distant background from two vantage points 6 months apart. Star A is closest to Earth.
Stellar parallax can be defined as the apparent change in position of a nearby star against the background of more distant stars as the Earth orbits the Sun. We view nearby stars from different positions in Earths orbit at different times of year. Once parallaxs of hundreds of stars were known and diagrams of the relationship between stellar luminosity and spectral types such as the Hertzsrpung-Russel diagram were made it became possible to estimate a stars absolute magnitude more or less.
The star Wolf 1061 has a parallax of 234 arcseconds while the star Ross 652 has a parallax of 170 arc seconds. To measure the distance to the nearest stars we must use the diameter of the earths orbit about the sun for our baseline. The nearest star is proxima centauri which exhibits a parallax of 0762arcsec and therefore is 131 parsecsaway.

Comments
Post a Comment